How does Ansible work?
Ansible is an automation tool that allows you to manage remote machines with modules. How do these modules work? Let’s take a look at the slack module as an example.
First we need ansible installed on our local machine:
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install ansible
Then download the slack module:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ansible-collections/community.general/refs/heads/main/plugins/modules/slack.py
Each module is a small self contained program. We can run these programs directly with the python interpreter.
python3 slack.py
It hangs there waiting for input. If we press control-D now we get an error:
{"msg": "Error: Module unable to decode stdin/parameters as valid JSON. Unable to parse what parameters were passed", "failed": true}
That’s a clue that it is waiting for JSON input. Let’s give it a valid JSON input:
python3 slack.py
{}
^D
We get a new error message:
{"msg": "Error: Module unable to locate ANSIBLE_MODULE_ARGS in JSON data from stdin. Unable to figure out what parameters were passed", "failed": true}
It is looking for ANSIBLE_MODULE_ARGS in the JSON:
python3 slack.py
{"ANSIBLE_MODULE_ARGS": {}}
^D
We finally get the arguments that it expects in the error message:
{"failed": true, "msg": "missing required arguments: token", "invocation": {"module_args": {"username": "Ansible", "icon_url": "https://www.ansible.com/favicon.ico", "link_names": 1, "validate_certs": true, "color": "normal", "domain": null, "token": null, "msg": null, "channel": null, "thread_id": null, "icon_emoji": null, "parse": null, "attachments": null, "blocks": null, "message_id": null}}}
Running this output through python -m json.tool makes it more readable:
{
"failed": true,
"msg": "missing required arguments: token",
"invocation": {
"module_args": {
"username": "Ansible",
"icon_url": "https://www.ansible.com/favicon.ico",
"link_names": 1,
"validate_certs": true,
"color": "normal",
"domain": null,
"token": null,
"msg": null,
"channel": null,
"thread_id": null,
"icon_emoji": null,
"parse": null,
"attachments": null,
"blocks": null,
"message_id": null
}
}
}
This matches the documentation for the module here: https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/modules/slack_module.html
We need to provide the token argument at least. Slack tokens are of the form abc/xyz/123 so let’s provide that:
python3 slack.py
{"ANSIBLE_MODULE_ARGS": {"token": "abc/xyz/123"}}
^D
{
"failed": true,
"msg": " failed to send {\"username\": \"Ansible\", \"icon_url\": \"https://www.ansible.com/favicon.ico\", \"link_names\": 1} to https://hooks.slack.com/services/[obscured]: HTTP Error 404: Not Found",
"invocation": {
"module_args": {
"token": "VALUE_SPECIFIED_IN_NO_LOG_PARAMETER",
"username": "Ansible",
"icon_url": "https://www.ansible.com/favicon.ico",
"link_names": 1,
"validate_certs": true,
"color": "normal",
"domain": null,
"msg": null,
"channel": null,
"thread_id": null,
"icon_emoji": null,
"parse": null,
"attachments": null,
"blocks": null,
"message_id": null
}
}
}
This error message shows that we are making some progress. It is contacting slack and rejecting the token. We can set up a real token using slack webhooks and try again.
To set up an incoming slack webhook we need to create an app here https://api.slack.com/apps.

Set the app name:
Then create in incoming webhook for that app here:
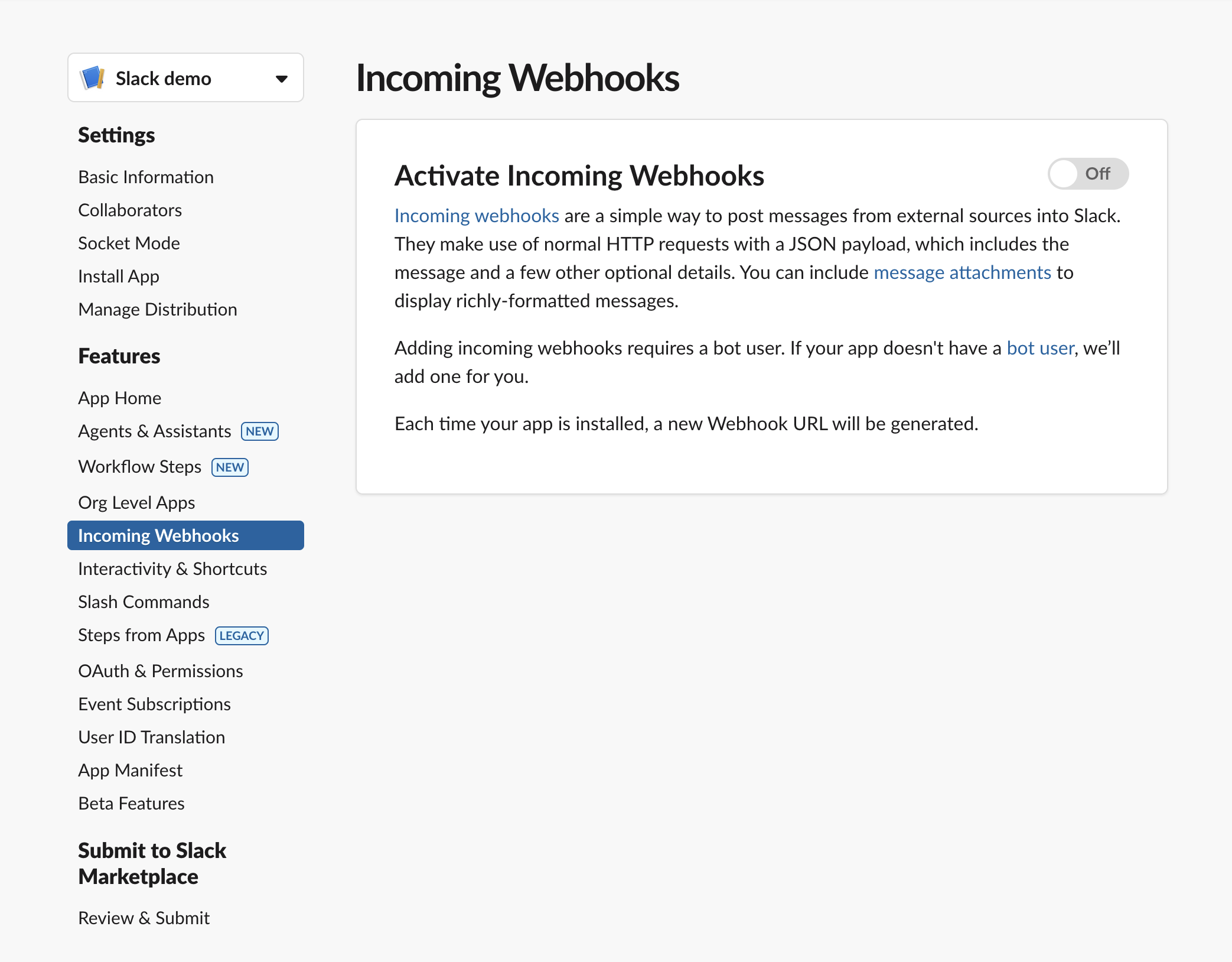
Turn it on:
Give it permission:
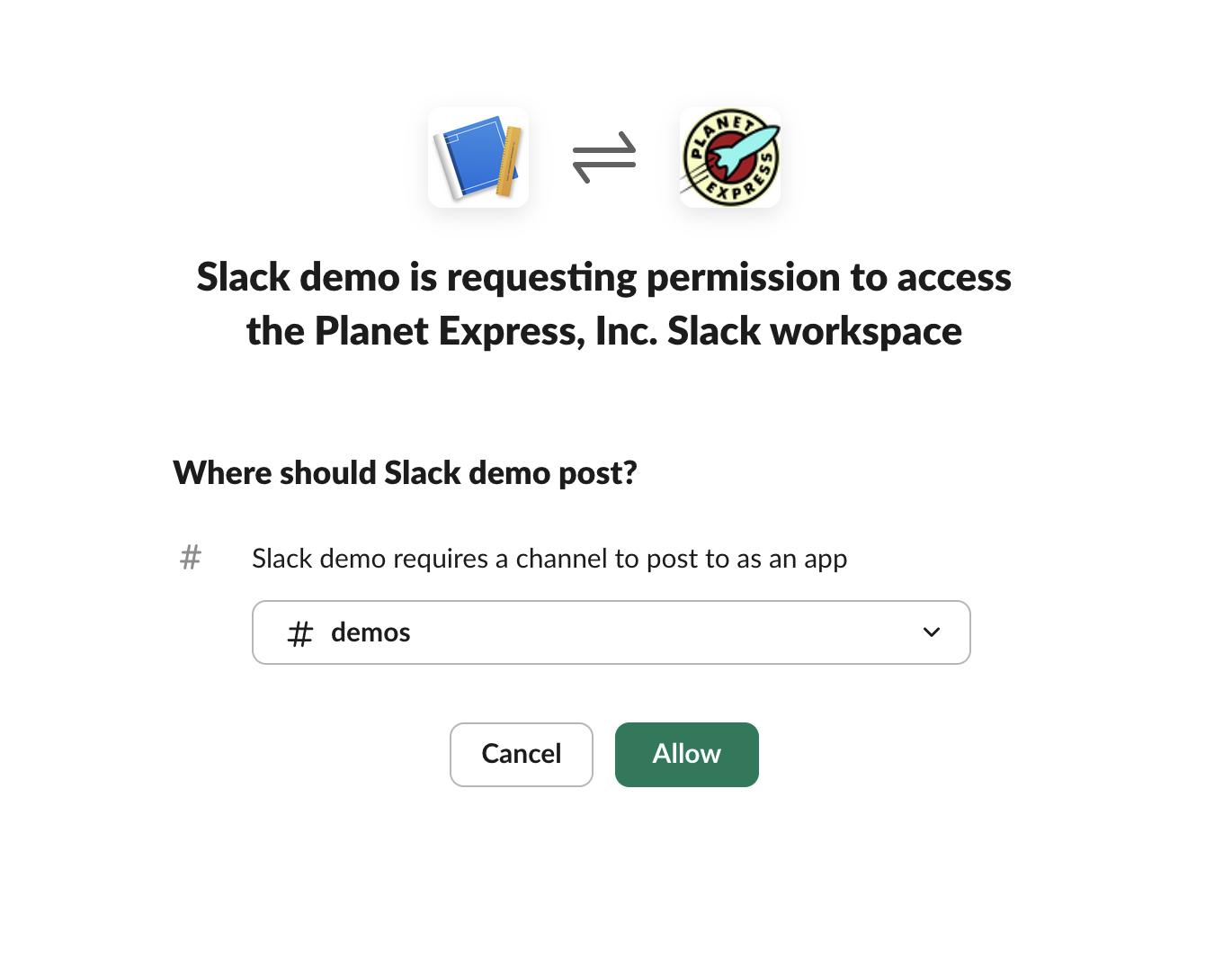
Then we can get the token from the webhook URL and paste it into the JSON as I do here (with the token redacted of course):
python3 slack.py
{"ANSIBLE_MODULE_ARGS": {"token": "REDACTED", "msg": "hello ben"}}
^D
This returns:
{
"msg": "OK",
"invocation": {
"module_args": {
"token": "VALUE_SPECIFIED_IN_NO_LOG_PARAMETER",
"msg": "hello ben",
"username": "Ansible",
"icon_url": "https://www.ansible.com/favicon.ico",
"link_names": 1,
"validate_certs": true,
"color": "normal",
"domain": null,
"channel": null,
"thread_id": null,
"icon_emoji": null,
"parse": null,
"attachments": null,
"blocks": null,
"message_id": null
}
}
}
Success! We have sent a message with the slack module by itself.

We have learned that Ansible modules are programs that expect JSON input on the standard input and write JSON to the standard output. If we look at the source code for the slack module here we see that it is written in Python, but modules can be written in other languages as well as long as they conform to this JSON protocol.
This leads to new questions:
- How do modules work on a remote host?
- Does the module need to run on the remote host or locally?
- How do we get the module to the remote host?
- Does python need to be installed there?
In this next post I will answer these questions.
